Basic of Energy Resource
We use energy resource every day. Energy resource is very fascinating. It surrounds us in differ en t forms such as heat, light and electricity. Any living organism relies on an external sources of energy e.g. Radiation from the sun in the case of green plants, chemical energy in some form in the case of animals (to be able to grow and reproduce).
Energy is always conserved, which means that it can neither be created nor be destroyed. Energy may be transformed from one form to another. There is no absolute measure of energy, because energy is defined as the work that one system does (or can do) on another. Thus, only the transition of a system from one state into another can be defined and thus measured.
Objectives
ENERGY
Energy is defi ned as th e ability or the capacity to do the work. When we eat, our bodies transform the food into energy to do the work. When we run or walk or do some work, we burn energy in our bodies. Cars, planes and machinery also transform energy into work.
Work means moving or lifting something, warming or lighting something. There are many sources of energy that help to run the various machines. Running water and wind can move turbines due to kinetic energy.
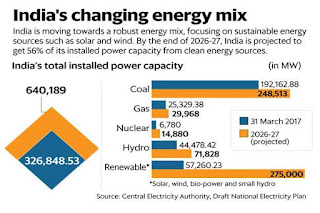
Different Energy Resources in INDIA 2017
Energy Measurement
One of the basic measuring blocks for energy is called a BTU or British Thermal Unit. BTU is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of the water by 1 degree Fahrenheit at sea level.
Energy can also be measured in Joules. One joule is the amount of energy needed to lift 1 pound to about 9 inches. It takes 1000 joules to equal a BTU.
1000 Joules = 1 Kilojoule = 1 BTU
*** Joule is named after an English physicist named James Prescott Joule who discovered that heat is a type of energy.
Energy Source
An energy source is a substance or a system that is capable of delivering net kilowatt hours of energy to the system. Gasoline is a net energy source. The various energy sources are "renewable energies" like biomass, bio-fuels,biogases
Energy Carrier
Energy carriers move energy in auseable form from one place to another. Batteries, flywheels, utility pumped storage and terrestrial hydrogen are typical examples. They are energy carriers or you may call them energy transfer systems because you first have to fill them with energy before you can empty them
*** Allenergy carriers consume significantly more existing old energy than they can return as new.
Energy Sink
An energy sink is any means that consumes more "old" energy than it return as new energy.
The solar photovoltaic PV system may be a net energy sink because PV has in totality consumed far more old energy than it has yet to deliver as new. If your solar panel is generating Rs. 10 worth of electricity a day and the interest cost is Rs. 12 a day, you have a net energy sink.
GRADES OF ENERGY
The electricity or electrical energy is capable of almost complete conversion into work while thermal energy is capable only of partial conversion into work. You can say that the electricity is of high quality or high grade of energy. Also the same quantity of energy after use has less capacity for work. In other words, you can say that it is the ability of energy to do work which set its quality.
EXAMPLES
1). OnekJ kJ
2). OnekJ kJ
High Grade Energy
When energy is concentrated in a small space, we call it high grade energy like electricity and chemical energy. The high grade energy should be used for high grade applications rather than low grade applications like heating of water.
The particles or molecules that store these forms of energy are highly ordered and compact.
Low Grade Energy
Low grade energy is characterized where the particles or molecules that store this form of energy are randomly distributed. For examples, heat is low grade energy.
Energy Use
You are our aware that energy is required for doing any kind of work. Energy lights our cities, powers our vehicles and run all kinds of machinery in industries. It provides thermal comfort in our homes, cooks our food, play our music and gives us pictures on television. You can't imagine present day life without energy. Energy is derived from various sources.
The use of an energy source depends upon the amount of energy available, ease of distribution, the extent to which energy can be concentrated and the convenience with which it can be used. We are responsible for the conservation, intelligent and safe use of energy.
We use energy resource every day. Energy resource is very fascinating
Energy is always conserved, which means that it can neither be created nor be destroyed. Energy may be transformed from one form to another. There is no absolute measure of energy, because energy is defined as the work that one system does (or can do) on another. Thus, only the transition of a system from one state into another can be defined and thus measured.
Objectives
- Explain the meaning of energy and its unit.
- Understand the various forms of energy.
- Know the world reserve of energy
- Describe the different energy sources.
ENERGY
Ener
Work means moving or lifting something, warming or lighting something. There are many sources of energy that help to run the various machines. Running water and wind can move turbines due to kinetic energy.
Different Energy Resources in INDIA 2017
Energy Measurement
One of the basic measuring blocks for energy is called a BTU or British Thermal Unit. BTU is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of the water by 1 degree Fahrenheit at sea level.
Energy can also be measured in Joules. One joule is the amount of energy needed to lift 1 pound to about 9 inches. It takes 1000 joules to equal a BTU.
1000 Joules = 1 Kilojoule = 1 BTU
*** Joule is named after an English physicist named James Prescott Joule who discovered that heat is a type of energy.
Energy Source
An energy source is a substance or a system that is capable of delivering net kilowatt hours of energy to the system. Gasoline is a net energy source. The various energy sources are "renewable energies" like biomass, bio-fuels,
Energy Carrier
Energy carriers move energy in a
*** All
Energy Sink
An energy sink is any means that consumes more "old" energy than it return as new energy.
The solar photovoltaic PV system may be a net energy sink because PV has in totality consumed far more old energy than it has yet to deliver as new. If your solar panel is generating Rs. 10 worth of electricity a day and the interest cost is Rs. 12 a day, you have a net energy sink.
GRADES OF ENERGY
The electricity or electrical energy is capable of almost complete conversion into work while thermal energy is capable only of partial conversion into work. You can say that the electricity is of high quality or high grade of energy. Also the same quantity of energy after use has less capacity for work. In other words, you can say that it is the ability of energy to do work which set its quality.
EXAMPLES
1). One
2). One
High Grade Energy
When energy is concentrated in a small space, we call it high grade energy like electricity and chemical energy. The high grade energy should be used for high grade applications rather than low grade applications like heating of water.
The particles or molecules that store these forms of energy are highly ordered and compact.
Low Grade Energy
Low grade energy is characterized where the particles or molecules that store this form of energy are randomly distributed. For examples, heat is low grade energy.
Energy Use
You are our aware that energy is required for doing any kind of work. Energy lights our cities, powers our vehicles and run all kinds of machinery in industries. It provides thermal comfort in our homes, cooks our food, play our music and gives us pictures on television. You can't imagine present day life without energy. Energy is derived from various sources.
The use of an energy source depends upon the amount of energy available, ease of distribution, the extent to which energy can be concentrated and the convenience with which it can be used. We are responsible for the conservation, intelligent and safe use of energy.
Comments