Energy is always conserved, which means that it can neither be created nor destroyed. Energy may be transformed from one form to another. The concept of energy and its transformations is extremely useful in explaining and predicting most natural phenomena.
where
🔺 E = W
Here, E is the amount of energy transferred and W represents the work done on the system. In this equation, you can see that all energy transferred in converted in to
🔺E = W + Q
Modes of Energy Conversion:-
The conversion of energy can be classified based on the stages involved in the energy conversion processes. This could be direct conversion, single stage conversion and multistage
Direct Energy Conversion
The three direct energy conversion processes. Photoelectric, Thermo-electric and Electro chemical.
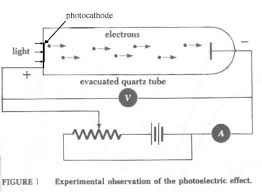
1). Photoelectric Energy Conversion:-
In photo-electric conversion, solar energy is directly converted into electricity. Solar energy (light) can be thought of made of quanta of light called photons. The energy conversion device is called a solar cell or solar photo-voltaic (PV) cell. A solar cell is made up of semiconductor material. When light strikes the junction (p-n junction) of a semi-conductor material, the voltage appearing across the junction of the cell. The energy of the photons gets converted into electrical energy.
*** The direct energy conversion was of immense importance in spacecrafts where solar PV cells were used to power the spacecrafts.
2). Thermo-electric Energy Conversion:-
Thermocouple devices are used to convert thermal energy directly into electricity. The principle of thermocouple is simple. When a junction made of two different metals (e.g. Copper and Iron)is heated , a voltage appears across the output terminals of the junction due to differential heating of the two different metals.
The efficiency of a thermo-electric converter may be written as follows.
3).Electrochemical Energy Conversion:-
The chemical energy can be directly converted into electricity. The device used is known as Fuel Cell.
Chemical → Fuel → Electrical
Energy Cell Energy
Multistage Energy Conversion:-
In multistage energy conversion, energy conversion take place in themultistage . For example, Electromechanical Conversion in which the electrical energy converted into mechanical energy and vice-versa. The energy conversion device is called an electric machine which is able to convert an electric energy into mechanical energy and vice versa.
Electric machines are of two types and are called as Generator and Motor
Generator: o convert mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a generator .
Motor:
Some of the important energy conversion processes are:-
In photo-electric conversion, solar energy is directly converted into electricity. Solar energy (light) can be thought of made of quanta of light called photons. The energy conversion device is called a solar cell or solar photo-voltaic (PV) cell. A solar cell is made up of semiconductor material. When light strikes the junction (p-n junction) of a semi-conductor material, the voltage appearing across the junction of the cell. The energy of the photons gets converted into electrical energy.
*** The direct energy conversion was of immense importance in spacecrafts where solar PV cells were used to power the spacecrafts.
2). Thermo-electric Energy Conversion:-
Thermocouple devices are used to convert thermal energy directly into electricity. The principle of thermocouple is simple. When a junction made of two different metals (e.g. Copper and Iron)
The efficiency of a thermo-electric converter may be written as follows.
Where, T1 is the temperature of hot reservoir and T2 is the temperature of the sink.
Z is called a figure of merit of the thermocouple.
3).
The chemical energy can be directly converted into electricity. The device used is known as Fuel Cell.
Chemical → Fuel → Electrical
Energy Cell Energy
Multistage Energy Conversion:-
In multistage energy conversion, energy conversion take place in the
Electric machines are of two types and are called as Generator and Motor
Generator
Motor
Some of the important energy conversion processes are:-
- Conversion of Heat into Electricity:
Thermoelectric - Conversion of Heat into Electricity: Geothermal Power
- Conversion of Heat into Electricity: Ocean Thermal Power
- Conversion of Gravitational Potential Energy into Electricity: Hydroelectric Dams
- Conversion of Kinetic Energy into Electricity
: Electric Generator - Conversion of
Chemical Energy - Conversion of
Chemical Energy : Lamp - Conversion of Nuclear Energy into Electricity
: Nuclear Power Plant - Conversion of Wind Energy into Electricity
: Wind Mills - Conversion of Solar Energy into Electricity
: Solar Cells or PV Cell - Conversion of Wave Energy into Electricity
: Wave Power
Video regarding: - Energy Conversions


Comments