When we try to understand energy, we have to understand energy resources and their limitations along with their impact on the environment. All the developed nations of the world are consuming more energy for their economic development as compared to developing nations.
We can help to save the environment by:-
1) Reducing the use of energy without affecting the progress.
2) Reducing the waste produced &
3) Using renewable energy sources.
1). The production of carbon dioxide when fossil fuels are used to generate energy and when fossil fuels are used to generate energy and when forests are cut down and burned.
2). The production of methane and nitrous oxide from agricultural activities, changes in land use and other sources.
3). The production of man made chemicals called halocarbons (CFCs, HFCs, PFCs) and other long lived gases such assulphur
1). Encouraging energy efficiency in industries, homes, offices, vehicles and agriculture.
2). Encouraging use of energy efficient technologies.
3). Good housekeeping measures.
4). Ensuring the interaction between energy, economy and environment.
5). Encouraging energy substitution which means use of renewable energy technologies as much as possible.
6). Reducing the usage of electricity, LPG, Petrol, Diesel etc.whenever
The Protocol states that "developed countries are committed, individually or jointly, to ensuring that their aggregate anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide equivalent emissions of greenhouse gases do not exceed amounts assigned to each country".
India's Greenhouse Gas Emissions:-
India has experienced a dramatic growth in fossil fuel emissions and the data compiled by various agencies shows an increase of nearly 5.9% since 1950. At present India is rated 6th largest contributor of carbon dioxide emissions of 0.93 tonnes per annum are well below the world average of 3.87 tonnes per annum. Fossil fuel emissions in India continue to result largely from coal burning.
The nuclear energy gets converted into mechanical energy and electricity resulting into waste heat loss to the environment.
Nuclear energy has one of the lowest impacts on the environment of any energy source because it does not emit air pollution, isolates its waste from the environment and requires a relatively small amount of land.
The concept ofgreenhouse effect
:
We can help to save the environment by:-
1) Reducing the use of energy without affecting the progress.
2) Reducing the waste produced &
3) Using renewable energy sources.
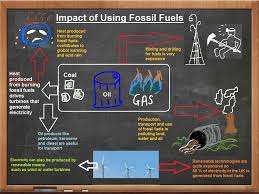
Environmental Impacts Of Fossil Fuels:-
1). Human Activities Responsible for Greenhouse Gases:-
The important activities responsible for releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere are:1). The production of carbon dioxide when fossil fuels are used to generate energy and when fossil fuels are used to generate energy and when forests are cut down and burned.
2). The production of methane and nitrous oxide from agricultural activities, changes in land use and other sources.
3). The production of man made chemicals called halocarbons (CFCs, HFCs, PFCs) and other long lived gases such as
2). Options for Limiting Emissions:-
The options available for limiting emissions to the environment are:1). Encouraging energy efficiency in industries, homes, offices, vehicles and agriculture.
2). Encouraging use of energy efficient technologies.
3). Good housekeeping measures.
4). Ensuring the interaction between energy, economy and environment.
5). Encouraging energy substitution which means use of renewable energy technologies as much as possible.
6). Reducing the usage of electricity, LPG, Petrol, Diesel etc.
3). Global Climate Change Treaty: The Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol experts that the industrialized nations should make efforts in reducing emissions of Green House gases. The six major greenhouse gases covered by the protocol are Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous oxide, Hydrofluorocarbons, Perfluorocarbons and Sulfur Hexafluoride.The Protocol states that "developed countries are committed, individually or jointly, to ensuring that their aggregate anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide equivalent emissions of greenhouse gases do not exceed amounts assigned to each country".
 |
| KYOTO PROTOCOL |
India has experienced a dramatic growth in fossil fuel emissions and the data compiled by various agencies shows an increase of nearly 5.9% since 1950. At present India is rated 6th largest contributor of carbon dioxide emissions of 0.93 tonnes per annum are well below the world average of 3.87 tonnes per annum. Fossil fuel emissions in India continue to result largely from coal burning.
4). Clean Development Mechanism (CDM)
The CDM enables developing countries to participate in joint greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation projects. Under this protocol, countries are required to reduce GHG emission to below their 1990 levels. The CDM enables these countries to meet their reduction commitments in a flexible and cost effective manner. It allows public or private sector entities invest in GHG mitigation projects in the developing countries. In return the investing parties receive credits or Certified Emission Reduction (CERs). |
| CDM |
Environmental Impacts of Nuclear Energy:-
The nuclear energy gets converted into mechanical energy and electricity resulting into waste heat loss to the environment.
Nuclear energy has one of the lowest impacts on the environment of any energy source because it does not emit air pollution, isolates its waste from the environment and requires a relatively small amount of land.
Environmental Impacts of Greenhouse Gases:-
The "greenhouse effect" is usually defined as the heating of the Earth's atmosphere due to the presence of greenhouse gases. The temperature of the Earth's has reportedly increased by about 0.5 C during the past country, a phenomenon referred to as Global Warming. After the 1997 Kyoto Protocol, the world has finally taken the first step in reducing emissions.The concept of
- Shorter - wavelength solar radiation from the sun passes through Earth's atmosphere.
- These radiations are absorbed by the surface of the Earth, causing it to warm.
- Part of the absorbed energy is then re-radiated back to the atmosphere as long wave infrared radiation.
- Some of these long wave radiations escape back into space, the radiation cannot pass through the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases absorb these waves and re-emits the waves downward, causing the lower atmosphere to warm.


Comments