Energy use in India is quite appreciable for commercial and industrial applications. The increase is almost 5% per year. The energy resources used are :
1). Radiant Energy:-
Video regarding- COAL
- BIOMASS (Wood and Cow dung)
- OIL (Petrol, Diesel, and Kerosene)
- ELECTRICITY (about 70% of electricity in India is generated by polluting coal.)
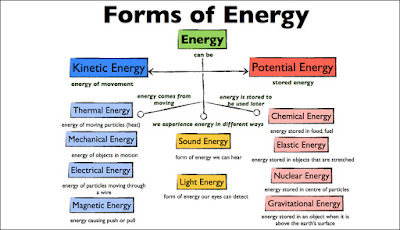
Energy exists in many forms. Broadly speaking, we can classify energy into two types, potential and kinetic energy.
Potential Energy
The potential energy is the stored energy and the energy of position (gravitational). Potential Energy exists in many forms.
1). Chemical Energy:-
The energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules is called chemical energy. The examples of stored chemical energy are petrol, diesel, kerosene, natural gas, coal, wood and other biomass. The stored chemical energy is released as heat when these fuels burn.
2). Nuclear Energy:-
The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom, the energy that holds the nucleus together is called nuclear energy. The examples are nucleus of uranium atoms. Modern societies are using nuclear energy in nuclear energy in nuclear power stations to generate electricity to power submarines and ships etc.
3). Stored Mechanical Energy:-
The energy stored in an object by the application of force is called stored mechanical energy. The examples of stored mechanical energy are compressed springs and stretched rubber.
4). Gravitational Energy:-
The energy by virtue of place or position is called gravitational energy. The water stored in a reservoir in a dam is the best example of the gravitational energy. This energy can be released when the flow of the river is controlled to produce electricity at a dam.
Kinetic Energy:-
The energy of motion of waves, electrons, atoms etc. is
1). Radiant Energy:-
The radiant is electromagnetic energy. You are familiar with X-rays, visible lights, radio waves, gamma rays etc. All these are radiant energy. Solar energy, which we will discuss in details in this course, is also an example of radiant energy.
2). Thermal Energy:-
The internal energy of substance is called thermal energy. Geothermal energy is an example of thermal energy.
1). Motion:-
The movement of substance from one place to another is energy associated with motion. The examples are wind energy and hydro power.
2). Sound:-
The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is called sound waves.
3). Electrical:-
The electrical energy is the movement of electrons. The examples include electricity and lighting.
*** You should remember:-
- Energy is all around us.
- Energy exists in many forms.
- Energy can be detected by our senses.
- Energy is stored in different situations.
- Energy can change form and can be used to do useful work.
- All changes in the universe involve the interaction between energy and matter.
Comments