Primary energy resources are those that are found in nature and mostly converted into secondary resources in industrial utilities. For example, Coal, Oil and Gas (primary energy resources) are converted into steam and electricity (secondary resources of energy) for various applications.
The principal energy resources on our plants are the fossil fuels like coals, oil, natural gas, biomass (such as wood, agricultural waste, etc.), water, wind and nuclear energy. Some uncommon energy resources include geothermal and tidal energy.
Video Regarding: - What are Energy Resources?
The principal energy resources on our plants are the fossil fuels like coals, oil, natural gas, biomass (such as wood, agricultural waste, etc.), water, wind and nuclear energy. Some uncommon energy resources include geothermal and tidal energy.
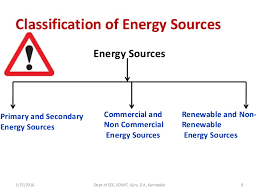
These energy resources are usually classified as:-
- Primary and Secondary Resources
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources
- Commercial and
Non-Commercial
1). Primary and Secondary Resources:-
Primary energy resources are tho se that are found in nature and mostly converted into secondary resources in industrial utilities. For example, Coal, Oil and Gas (primary energy resources) are converted into steam and electricity (secondary resources of energy) for various applications.
Primary energy resources are th
The energy resources such as coal, oil and gas cannot be replenished within a reasonable time span and are likely to be depleted with time. They are often referred to as fossil fuels as they are found underground. They have formed over millions of years, but the rate they consumed is much higher than they formed. They are practically
On the other hydro energy, wind energy, biomass energy, solar energy, tidal and geothermal energy are perpetual sources as they do not exhaust. All these sources are dependent upon sun dependent and they will continue to exist as long as the sun lasts. They are identified as renewable. They are better termed as conventional or alternative energy sources. So these resources will not be depleted.
3). Commercial and
The energy resources that are available in the market for a definite price are known as commercial energy resources. These include coal, oil, natural gas, electricity and refined petroleum products. There are certain energy resources that not available in the commercial market for a price. These are called non-commercial resources.
For example cow dung, agricultural wastes, solar energy for drying food products, animal power for transport, threshing, lifting etc.
For more


Comments