- There are other energy sources which are not so popular but are now gaining importance such as:-
- Hydrogen Energy
- Chemical Sources of Energy (Fuel Cells)
- Geo-Thermal Energy
- Ocean and Tidal Energy
- Biofuels
- Animal Energy
Hydrogen Energy:-
In the case of Hydrogen energy, electricity is produced through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen can be produced from the electrolysis of water using solar energy. It can be extracted from sewage gas, natural gas, naptha biogas
Hydrogen as Fuel:-
Hydrogen as a gas is so much lighter than air that it rises fast and is quickly atmosphere result
Point to Remember:
- Hydrogen has the highest energy content of any common fuel by weight (about 3 times more than gasoline)
- Hydrogen has the lowest energy content by volume (about 4 times less than gasoline).
Electricity is the most well-known energy carrier. Like electricity, hydrogen is an energy carrier and must be produced from another substance. Hydrogen is not currently widely used but emissions but
Hydrogen Fuel Cells produce Electricity:-
Hydrogen fuel cells (batteries) are being used as a source of electricity. They are very efficient but
Hydrogen Use in Vehicles:-
Fuel cells are based on the electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, water vapor and heat. The byproduct of the reaction can be re-utilized by the fuel cell system. Fuel cells are efficient, environmentally friendly and reliable for power production. The use of fuel cells has been demonstrated for stationary/ portable power generation and other applications.
Fuel cells are different from electrochemical cell batteries in that they consume reactant from an external source, which must be replenished. By contrast, batteries store electrical energy chemically and hence represent a closed system.
Many combinations of fuel and oxidant are possible. A hydrogen cell uses hydrogen as fuel and oxygen (usually from air) as oxidant. Other fuels include hydrocarbons and alcohols. Other fuels include hydrocarbons and alcohols. Other oxidants include chlorine and chlorine dioxide. Fuel cells are a simple, low-cost devices and can produce power as long as the fuel and oxygen are supplied to it.
Fuel Cell Components:-
There are three main components of a fuel cell system. These are:
- Hydrogen source
- Fuel Cell stacks
- Power inverter
The hydrogen can be produced through electrolysis of water by using renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind generators. The fuel cell stack converts the hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, water vapor and heat. An inverter converts the DC electricity from fuel cells into AC electricity that most equipments requires.
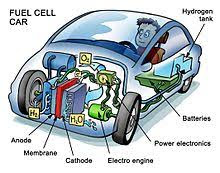 |
| FUEL CELL in CAR |
Advantages of Fuel Cells:-
Fuel Cells have a number of advantages over other technologies for power generation. Some of the important advantages are:-
- Use less fuel as compared to other competing technologies.
- Emit no pollution when used.
- Quiet operation without noise pollution.
 |
| FUEL CELL |
Geothermal Energy:-
There are two large sources of energy. One is the sun
We can recover this heat as steam or hot water and use it for various applications like power generation and direct heat applications. Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source because the heat is continuously produced inside the Earth.
In India, Northwest Himalayas and the west coast are considered geothermal areas. The Geothermal Survey of India has already identified more than 350 hot spring sites, which can be explored as areas to tap geothermal energy.
Like volcanoes and fumaroles
 |
Geothermal energies are of two types: - High and Low grade
- High grade: - It is the heat due to the earth pressure that turns water into steam.
- Low grade: - It is the heat within the earth's crust. This heat is actually stored solar energy.
Use of Geothermal Energy:-
The main areas where geothermal energy is being used are:-
- Direct use as heating systems: Geothermal energy is used to heat water springs or reservoirs near the surface.
- Electricity generation by power plants: This application requires water or steam at a very high temperature.
- Geothermal heat pumps: The geothermal energy is used where the stable ground or water temperatures near Earth's surface are available to control temperatures in a building above ground. A heat pump is a mechanical device used for heating and cooling purposes. The heat pump operates on the principle that heat can be extracted from a warmer temperature to a cooler temperature. A geothermal heat pump uses the earth to warm us in the winter and cool us in the summer.
Ocean and Tidal Energy:-
These are the two main sources of ocean renewable energies. The other ocean energies are wave energy, ocean current energy, offshore wind and ocean thermal gradient energy.
The vast potential of the energy of the seas and oceans which cover about three fourth of our planet can make a significant contribution to meet our energy needs. Ocean energy can be used to generate electricity in an environment-friendly manner.
Waves are caused by the wind blowing over the surface of the ocean. There is tremendous energy in the ocean waves. The wave energy converters are used to extract the power of ocean waves and convert it into electricity. Typically, these systems use either a water column or some type of surface to capture the wave power.
Waves are caused by the wind blowing over the surface of the ocean. There is tremendous energy in the ocean waves. The wave energy converters are used to extract the power of ocean waves and convert it into electricity. Typically, these systems use either a water column or some type of surface to capture the wave power.
Ocean Thermal Energy:-
Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) systems exploit temperature differences between warmer, surface layers and colder, deep layers of the ocean. All OTEC designs require a large-diameter intake pipe to pump cold water to the surface. They employ a variety of heat-exchange cycles to drive a turbine and generate electricity. |
| OTEC |
Tidal Energy:-
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun and the rotation of the earth. Thus, tidal energy is the utilization of the moon and sun's gravitational forces - as tides are formed by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the oceans of the rotating earth.
Nearshore, water levels can vary up to 40 feet due to tides. A flood tide is one that is coming in or rising and an ebb tide is one that is going out. Thus, tidal energy takes advantage of the daily ebb and flow of tides and of localized examples of water in motion. The gravitational pull of the moon drives tidal flows. Tidal energy is one of the oldest forms of energy used as evidence of tide mills from before 1100AD has been found along the coast of France, Spain and the UK.
The process of generating electricity from the tidal energy may be understood by the following steps:-
- When the tides come in, water flows through a sluice into a storage pond.
- When the tides go back out, the water flows back into the sea by passing through a turbine generating electricity.
 |
| Tidal and Wave Energy |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tidal Energy:-
Advantages:-
The important advantages of tidal energy are:-
- Tidal energy does not require any fuel.
- The economic life of a tidal plant is about 75 to 100 years as compared to about 35 years of a conventional fossil fuel plant.
- Tidal energy is clean and renewable.
- Tidal energy is non-polluting. A tidal barrage can prevent approximately one million tons of carbon dioxide per TWH generated.
Disadvantages:-
The important disadvantages are:-
- Tidal energy affects the ecosystem.
- Tidal energy leads to damage like reduced flushing and
erosion which - The alteration of tidal currents also affects the habitat of the seabirds and the fish.
BIOFUELS:-
Biofuels are liquid or gaseous fuels. They are manufactured from biomass, such as agricultural crops and the biodegradable parts of the waste. Biofuels can replace fossil fuels, such as petrol or diesel either totally or partially. The biofuels have been used in combustion engines way back over 100 years ago.
There are many types of biofuels. The well-known biofuels are biodiesel, bioethanol and biogas. Ethanol is generally produced from sugar cane or grain. In Brazil, Ethanol is manufactured from sugar
Ethanol is an alcohol that can be blended (up to 5%) with petrol, without any engine modifications required. Biofuels are classified as 1st generation and 2nd generation biofuels.
1st-Generation Biofuels:-
 |
| BIOFUELS |
The biofuels are defined based on the biomass from which these are produced. The biofuels produced from sugar, starch or oil-based crops or residues are known as 1st-generation biofuels. The examples include biodiesel from rapeseed oil or sunflower oil and alcohol from sugar beets or corn. The majority of 1st-generation achieves Carbon Dioxide emission reductions of around 30-50% compared to fossil fuels.
2nd-Generation Biofuels:-
The biofuels produced from the woody parts of plants or trees are known as 2nd-generation biofuels. These biofuels can achieve Carbon Dioxide emissions reduction od
Biofuels are attractive alternatives to petrol and diesel for use in automobiles. The Government of INDIA as now permitted the use of 5% ethanol blended petrol. Ethanol produced from molasses/cane juice, when used as a fuel will reduce the dependence on crude oil and help in reducing pollution.
Most of the fossil fuels which are used in biological nature. Biofuel does not add to the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and give up the same amount when burnt. This is why biofuels are considered to be Carbon dioxide neutral. The type or biofuels used will depend on a number of factors like available feedstock and the energy that can be used locally.
Animal Energy:-
Domesticated animals are used in drawing heavy loads. Draft animals were in common use in Mesopotamia, before 3000 BC for farm work and for pulling wheeled vehicles. Their use spread to the rest of the world over the following 2,500 years.
Some horses such as the Belgian horse, the Clydesdale, the Suffolk, the Shire and the Percheron have been bred to serve as Draft animals. The Asian water buffalo is probably the most important draft animal in the world today. Many of some 165 million domesticated water buffalo worldwide are used as draft animals, tropical Asia, where they assist in the production of rice.
The role of draft animals in agriculture in less developed regions of the world continues because of the advantages they offer, their feed is easily grown and commonly available, little maintenance of the animals is required, their manure is a valuable resource for the farmer and the animal itself may become a source of food or other products at the end of its useful life.
A draught or draft animal is an animal used for its physical (i.e. Muscular) power, as in transport and haulage, such as pulling carts or sleds, plowing fields and hauling goods. Animals are also used for animal-powered transport, for the movement of people and goods. People ride some animals directly as mounts, use them as pack animals to carry goods or harness one or a team to pull vehicles. Such animals are sometimes known as beasts of burden.
 |
| Animal Energy |
Pack Animals:-
These often belong to the same species as mounts or harness animals, though animals such as horses, mules, donkey, or the Arabian camel may be of specialized breeding for packing. Other species are only used to carry loads, including Ilamas in the Andes and the Bactrian camel in Central Asia.
Bovines include water buffalo (as distinct from bison and the extremely dangerous African Cape buffalo both of which cannot be domesticated, oxen, bullock and yaks (the latter adapted to extreme conditions in the Himalayas). Other species include dogs, reindeer and goats.
Other Draught Animals:-
Animal power is also used to drive machines and devices and for ploughing, especially oxen. Water buffalo in tropical or very wet subtropical, areas help in rice-growing. Elephants are still used for logging in South-East Asia.
Animal used for different Purpose:-
As predatory species are naturally equipped to catch prey, this is a further use for animals and birds. This can be done either for sustenance or sport, to reduce the population of undesired animals (pests) that are considered harmful to crops, livestock or the environment.
Hounds and other dogs are used to kill and fetch prey. Certain breeds have been bred for this task. Mousers (domestic cats used for hunting small rodents and birds) are one of the oldest working animals having protected food supplies from pests since the foundation of human agriculture. Ferrets prey on creatures living in burrows such as rabbits and hares.
Dogs with their highly developed sense of smell are used to catch human 'prey' such as escaped prisoners or people lost in remote areas. They are also used to find people who are trapped, such as in avalanches or collapsed buildings.
Horses are used in remote areas to help human searches cover large areas of rugged terrain. Their natural awareness of their surroundings will often alert human handlers to the presence of anything unusual, including lost hikers, hunters or other.

Comments