Green Building
Green Building does not refer to building which are green in colour or have been constructed with green parks around. It refers to a conscious practice of addressing the issue of resource conservation in an integrated and scientific manner. By definition, a green building is one which uses less water, optimizes energy efficiency, conserves natural resources, generates less waste and provides healthier spaces for occupants, as compared to a conventional building.
Modern-day building have a tendency to use designs and materials which are resource-intensive and are quite often operate in isolation with the nature. Such buildings are very poor in energy efficiency and generate a lot of waste, adding to faster depletion of natural resources. Thus, building are seen today as one of the major pollutants to affect urban air quality and contribute to climate change.
A green building depletes very little of the natural resources during its construction and operation. The aim of a green building design is to:-
91-100 Five Star
1). Energy collection and storage is by natural means. .
2). Energy distribution is by natural means.
3). The system mostly work without external power.
4). Daylight is extensively used.
5). Passive cooling and heating can be inherent in the building construction.
6). Energy flow by natural means.
3). The system uses external power.
4). Daylight is extensively used.
5). Passive cooling and heating can be inherent in the building construction.
6). Energy flow from collector to storage or from storage to living space is forced type.
1). Energy collection and storage is by forced means.
2). Energy distribution is by forced means.
3). The system works with external power.
4). Less use of daylight.
5). Heating and cooling systems and their controls are not an integral part of the building construction.
6). Energy flow within the system is by forced means.
Modern-day building have a tendency to use designs and materials which are resource-intensive and are quite often operate in isolation with the nature. Such buildings are very poor in energy efficiency and generate a lot of waste, adding to faster depletion of natural resources. Thus, building are seen today as one of the major pollutants to affect urban air quality and contribute to climate change.
 |
| GREEN BUILDING |
- Minimize the demand on non-renewable resources and maximize the utilization efficiency of these resources when in use maximize reuse and recycling of available resources.
- Utilization of renewable resources
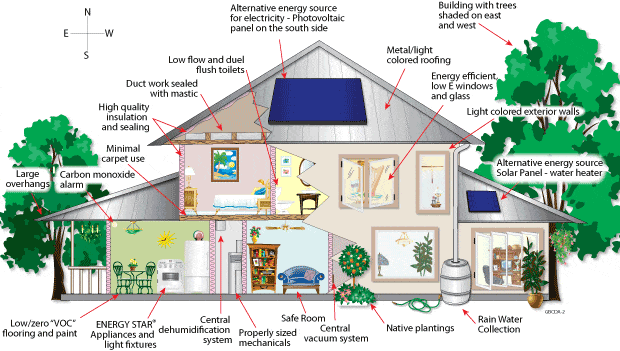
It maximizes the use of efficient building materials and construction practices, optimizes the use of on-site sources and sinks by bio-climatic architectural practices, uses efficient equipment to meet its lighting, air-conditioning and other needs, maximizes the use of renewable sources of energy, sources of energy, uses efficient waste and water management practices and provides comfortable and hygienic indoor working conditions. In particular, the following aspects of the building design are looked into in an integrated way in a green building:
- Site planning
- Building envelope design.
- Building system design including that of HVAC(heating, ventilation and air conditioning), lighting, electrical and water heating.
- Integration of renewable energy sources to generate energy onsite.
- Water and waste management.
- Selection of ecologically sustainable materials (with high recycled content, rapidly renewable resources with low emission potential, etc.)
- Indoor environmental quality (maintain indoor thermal and visual comfort and air quality).
 |
BENEFITS OF GREEN BUILDINGGREEN BUILDING RATING SYSTEM:- |
Building Rating System have been developed and found quite effective. Most of the internationally devised rating systems have been tailored to suit the building sector of the country where they were developed. Both the rating system promote whole-building approach to sustainability and environment protection and provides tools to design, construct and operate green buildings.
LEED Rating System
It is an adaption of US-based LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) Rating System and is being implemented by Indian Green Building Council. The certification level is as per the points scored by the building based on the specified criterion.
Point Scored LEED Certification level
26-32 Certified
33-38 Silver
39-51 Gold
52 or more Platium
GRIHA Rating System:-
Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment is promoted by The Energy Resource Institute (TERI) and the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Govt. of India. GRIHA has a 100 point system consisting of some core points which are mandatory to be met while the rest are optional points, which can be earned by complying with the commitment of the criterion. Different level of certification (one star to five star) is awarded based on the number of points earned.
Point Scored Number of Stars Earned by the building
50-60 One Star
61-70 Two Star
71-80 Three Star
81-90 Four Star
91-100 Five Star
SOLAR BUILDING DESIGN ELEMENTS:-
The building systems may be broadly classified into three categories as mentioned below:-
- Passive building
- Active building
- Hybrid building
The basic philosophy in solar building design is that it uses structure's windows, walls and floors to collect, store and distribute the sun's heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. Any solar building includes five distinct design elements.
A Collector:- It is the large glass area through which sunlight is allowed to enter the building.
An Absorber:- It is the dark surface of the storage element that absorbs the solar heat.
A Thermal Mass:- The material that stores the absorbed heat. This can be masonry materials such as concrete, stone, brick or a water tank.
A Heat Distribution System:- The heat distribution could be natural using the concept that heat flows from warmer materials to cooler ones (through conduction, convection and radiation) until there is no longer a temperature difference between the two.
A Control Mechanism:- This is needed to regulate the amount of sunlight entering the building. This can be as simple as roof overhang designed to allow more sunlight to enter in the winter, less in the summer.
Broad Features of Buildings System
Passive System:-
Passive System:-
1). Energy collection and storage is by natural means. .
2). Energy distribution is by natural means.
3). The system mostly work without external power.
4). Daylight is extensively used.
5). Passive cooling and heating can be inherent in the building construction.
6). Energy flow by natural means.
Hybrid System:-
1). Energy collection and storage can be by natural means.
2). Energy distribution is by mechanical means.
2). Energy distribution is by mechanical means.
3). The system uses external power.
4). Daylight is extensively used.
5). Passive cooling and heating can be inherent in the building construction.
6). Energy flow from collector to storage or from storage to living space is forced type.
Active System:-
1). Energy collection and storage is by forced means.
2). Energy distribution is by forced means.
3). The system works with external power.
4). Less use of daylight.
5). Heating and cooling systems and their controls are not an integral part of the building construction.
6). Energy flow within the system is by forced means.
Solar Building Systems:-
 |
| SOLAR BUILDING SYSTEMS |
Solar Heating Systems:-
 |
| SOLAR HEATING SYSTEMS |
Solar Cooling Systems:-
 |
| SOLAR COOLING SYSTEMS |
Comments