Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen is the most abundant. Hydrogen gas has remarkable characteristics including colorless, tasteless and invisible that make it hotly pursued. It can also be transformed into a renewable, nonpolluting and zero-emission energy resource. It's viewed as the foundation of the new energy economy. The quest for hydrogen energy started way back in 1776 by the British researcher Henry Cavendish.
He initially recognized it as a particular component after he created hydrogen gas by oppressing zinc metal to hydrochloric corrosive. Henry Cavendish made another wonderful disclosure during an exhibition to the Royal Society of London when he acquainted a sparkle with hydrogen gas, delivering water simultaneously. This noteworthy advancement prompted his decision that water (H2O) is made out of hydrogen and oxygen. From that point forward, hydrogen innovation has filled quickly, and today, it is utilized as a fuel source to control vehicles, electric frameworks, and the creation of unadulterated water.
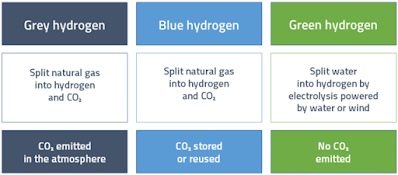 |
| Types of Hydrogen |
Hydrogen's science is extremely basic a solitary molecule is comprised of just a proton and an electron. In a vaporous structure, it tends to be signed as a fuel. It very well may be put away in power cells that create touchy energy and drive rockets and spaceships. It is unstable and burnable, and extremely, incredible.
Hydrogen can be put away cryogenically (frozen) or in compacted air compartments as a gas. It takes a ton of extra room to house huge measures of hydrogen. This is on the grounds that the particles are far separated, and the gas is lightweight, making it extremely spread out. To contain a similar measure of hydrogen in a chamber as gas, for instance, makes a lot heavier holder.
Energy Carrier
Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not an energy source, and can deliver or store a tremendous amount of energy. Hydrogen can be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, or power, and heat. Today, hydrogen is most commonly used in petroleum refining and fertilizer production, while transportation and utilities are emerging markets.
Production Pathways
Most hydrogen can likewise be created through steam methane improving, a high-temperature measure in which steam responds with a hydrocarbon fuel to deliver hydrogen.
Another normal hydrogen creation technique takes water and isolates the particle H2O into oxygen and hydrogen through a cycle called electrolysis. Electrolysis happens in an electrolyzer, which works similarly to a power module in an invert—rather than utilizing the energy of a hydrogen atom, similar to an energy component does, an electrolyzer produces hydrogen from water particles.
Organic cycles can likewise create hydrogen through natural responses utilizing microorganisms like microbes and microalgae. In these cycles, microorganisms devour plant material and produce hydrogen gas.
There are numerous approaches to create hydrogen utilizing daylight, including photobiological, photoelectrochemical, photovoltaic-driven electrolysis, and sun-based thermochemical measures.
Hydrogen can be produced from diverse, domestic resources including fossil fuels, biomass, and water electrolysis with electricity. The ecological effect and energy productivity of hydrogen rely upon how it is delivered. A few tasks are in progress to diminish costs related to hydrogen creation.
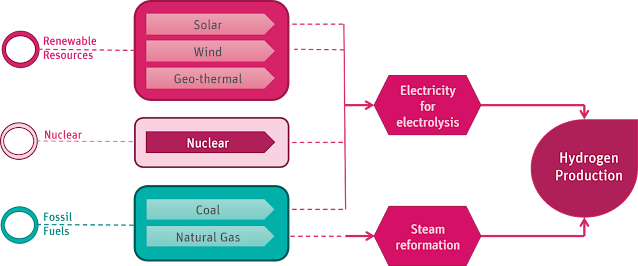 |
| Hydrogen Production |
There are a number of ways to produce hydrogen:
Natural Gas Reforming/Gasification: Synthesis gas, a combination of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and a modest quantity of carbon dioxide, is made by responding flammable gas with high-temperature steam. The carbon monoxide is responded with water to deliver extra hydrogen. This strategy is the least expensive, generally productive, and generally normal. Gaseous petrol improving utilizing steam represents most of the hydrogen delivered in the United States every year. Union gas can likewise be made by responding coal or biomass with high-temperature steam and oxygen in a compressed gasifier, which is changed over into vaporous segments—an interaction called gasification. The subsequent combination gas contains hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which is responded with steam to isolate the hydrogen.
Electrolysis: An electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. If the electricity is produced by renewable sources, such as solar or wind, the resulting hydrogen will be considered renewable as well and has numerous emissions benefits. Capacity to-hydrogen projects are taking off, where abundance sustainable power, when accessible, is utilized to make hydrogen through electrolysis.
Electrolysis: An electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. If the electricity is produced by renewable sources, such as solar or wind, the resulting hydrogen will be considered renewable as well and has numerous emissions benefits. Capacity to-hydrogen projects are taking off, where abundance sustainable power, when accessible, is utilized to make hydrogen through electrolysis.
Renewable Liquid Reforming: Renewable liquid fuels, such as ethanol, are reacted with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen near the point of end-use.
Fermentation: Biomass is converted into sugar-rich feedstocks that can be fermented to produce hydrogen.
Renewable Liquid Reforming: Renewable liquid fuels, such as ethanol, are reacted with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen near the point of end-use.
Fermentation: Biomass is converted into sugar-rich feedstocks that can be fermented to produce hydrogen.
A number of hydrogen production methods are in development:
High-Temperature Water Splitting: High temperatures generated by solar concentrators or nuclear reactors drive chemical reactions that split water to produce hydrogen.
Photobiological Water Splitting: Microbes, such as green algae, consume water in the presence of sunlight, producing hydrogen as a byproduct.
Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: Photoelectrochemical systems produce hydrogen from water using special semiconductors and energy from sunlight.
The essential test for hydrogen creation is diminishing the expense of creating advancements to make the subsequent hydrogen cost serious with customary transportation powers. Government and industry innovative work projects are diminishing the expense just as the natural effects of hydrogen creation advances. Take in additional about hydrogen creation from the Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office.
Distribution
Pros
- Zero ozone-depleting substance emanations when utilized.
- Interest for hydrogen has been consistently developing the most recent couple of many years
- Hydrogen delivered from environmentally friendly power sources is being created.
- Preferred efficiency over fuel, and more energy thickness/yield
- Less expensive pipeline (per mile) costs contrasted with unrefined petroleum pipeline costs
- Doesn't have huge transmission corruption issues whenever delivered locally and utilized before long creation
- Can be utilized deftly, and in supplement to other fuel sources.
- Power devices have low upkeep, and low energy drop off (contrasted with other fuel sources)
- Size of power devices is a benefit
- Offers a chance to lessen outside or unfamiliar reliance on a fuel hotspot for certain nations
- Can be utilized as an approach to store and utilize surplus environmentally friendly power sometime in the future.
- Low harmfulness openness hazard
- Can be utilized distantly in places without admittance to the power network
- Spillage from certain kinds of appropriation pipes aren't relied upon to be a critical issue
- Can be shipped and sent out – making it a tradable energy product.
Cons
- Subject to essential fuel sources to create hydrogen
- Not a totally perfect/efficient power fuel source at the present time (gaseous petrol and coal are a portion of the main fuel sources used to make hydrogen)
- Is an expensive method to really make energy – cost is maybe the greatest obstruction
- Fluid hydrogen is less energy-thick than some different kinds of energizes
- Has a few vulnerabilities and questions.
- Non privately created hydrogen can have energy misfortune issues
- The current foundation we have in numerous urban communities all throughout the planet isn't viable with hydrogen fuel
- Hydrogen doesn't perform well in specific temperatures and conditions.
- Restricted accessibility and access issues
- Can have some regrettable natural effects
- Needs a consistent fuel source
- Reach (distance of movement) might be restricted in hydrogen fuel vehicles at this moment
- Potential security issues (freeze consumption, combustibility, and now and again, the danger of a hydrogen station detonating)
- Possible issues of hydrogen inside gas pipes
- Singular nations may confront singular difficulties in creating more hydrogen, or utilizing more hydrogen energy
- Hydrogen is the least difficult and most bountiful component on earth—it comprises just a single proton and one electron. Hydrogen can store and convey usable energy, yet it doesn't normally exist without anyone else in nature and should be created from intensifies that contain it.
Uses for Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the primary component in the occasional table. Its nuclear number is one and its weight is 1.008. It is one of the steady flammable gas accessible in the universe. Plus, it is additionally essential for some biomolecules like carbs, proteins, fats, and so forth Thus, it has a wide assortment of employments as portrayed beneath.
1. Gas welding: A typical utilization of hydrogen gas is in the gas welding measure. It is utilized in this sort of welding to produce a high temperature of 4000°C. This high temperature prompts the softening of metals and accordingly joining the wrecked surfaces.
Other than creating heat, hydrogen additionally goes about as a safeguarding gas. Since metals at high temperatures are exceptionally responsive, hydrogen keeps them from responding with different components like nitrogen, carbon during the interaction. This interaction is likewise called nuclear hydrogen welding.
2.As fuel for automobiles:: Hydrogen fuel is a zero-outflow fuel that consumes on response with oxygen. It is an astonishing idea which means to control the autos by utilization of hydrogen rather than petrol fills.
This innovation is being created for use in huge scope as a substitute for petrol oils based motors. The upside of this innovation is the absence of air contamination as there is no hurtful gas discharged by start. The hydrogen energy component innovation is additionally utilized in submarines, bicycles, and so forth
3.In petroleum refinery:: Hydrogen gas is generally utilized in the oil business to eliminate sulfur content. Furthermore, it is likewise utilized for hydroisomerization, wherein typical paraffin is changed over to isoparaffin. Dearomatisation to change over fragrant to cycloalkanes. Hydrocracking to break long-anchor hydrocarbons to more limited ones.
4. Ultraviolet lamps: Hydrogen gas as deuterium is utilized in deuterium curve lights. These lights are utilized to deliver bright light. These lights have a tungsten fiber, which produces heat. The warmth in the bulb invigorates the deuterium particles (H²), which produce light in the bright area. These lights are utilized unequivocally in the spectroscopic investigation in labs.
5. As a reducing agent: Hydrogen goes about as both an electro-negative and electropositive component. This electro-positive nature makes it helpful in redox responses. The expansion of hydrogen is named as decrease, while evacuation is called oxidation.
6. In chemical analysis: Hydrogen is utilized in different strategies for synthetic examination. It is utilized in the Hydrogen terminal for titrations by potentiometry. Here hydrogen gas is passed at a steady speed at one air pressure into the reference cathode. The immaculateness of the hydrogen can influence the examination of these potentiometric titrations.
These strategies incorporate particularly the nuclear assimilation spectroscopy. Here the hydrogen is utilized as fuel to create heat during the time spent experimentation. The capacity of hydrogen to touch off is utilized in creating the nonpartisan iotas all the while.
7. In structural identification: Many mixtures have complex science. Various strategies are utilized to consider the design and the idea of connections between the particles and the atoms. Atomic attractive reverberation (NMR) is one of the methods which abuses the proton character to characterize the sub-atomic design. The strategy is additionally called proton NMR. The presence of hydrogen in numerous bio-atoms is used for this reason. Consequently, the presence of hydrogen helps in the primary ID.
8. Gas chromatography: Hydrogen is one of the gases which can be utilized as a versatile stage in gas chromatography. This strategy is utilized to isolate unstable substances from a combination for distinguishing proof.
9. Deuterium for electricity generation: as of now seen previously, the isotope of hydrogen is utilized to make substantial water (D2O). This weighty water is utilized in atomic reactors as a coolant and furthermore atomic arbitrator to hinder the neutrons.
10. In balloons: One of the principal employments of Hydrogen gas was in flying hot inflatables noticeable all around.
Because of its lightweight, minimal expense, hydrogen gas was utilized noticeable all-around inflatables for flight. Hydrogen was utilized in tourist balloons. The tourist balloons.
However, because of its hazardousness, it is being supplanted by helium. Helium is steady gas and furthermore one of the individuals from monoatomic components. In contrast to hydrogen, it is exceptionally non-responsive.
11. As rocket fuel for space programs: Hydrogen is utilized as the signature fuel for the American space program. It is incredible fuel for rockets. It has the most minimal atomic weight and is said to ignite with outrageous power. In mix with oxygen, it is said to yield the most noteworthy explicit drive corresponding to the measure of fuel burned-through.
12. In mass destructive bombs: This may not be the utilization of people with the exception of obliteration. In any case, it has been created as an amazing weapon of mass obliteration. The haze of nuclear bomb explosion. Testing of a nuclear bomb by the US. It depends on the rule of an atomic combination of hydrogen particles isotopes.
13. Hydrogen peroxide: This is a hydrogen compound in blend with oxygen as H2O2. Hydrogen peroxide is a routine disinfecting specialist utilized in the facility and emergency clinic. It is essentially utilized for cleaning wounds, cuts and other harmed tissue partitions.
Furthermore, in science, you will find out about hydrogen bonds, which are frail powers of fascination between atoms. It exceptionally consolidates with oxygen and, to a little degree, with nitrogen molecules to deliver these fascination powers. In research, it is likewise utilized for testing the counter oxidant capability of chemicals like catalase.
Comments