The electric vehicle is a vehicle that runs on electricity alone. Such a vehicle does not contain an internal combustion engine like the other conventional vehicles. Instead, it employs an electric motor to run the wheels. These vehicles are becoming very popular nowadays. They are considered to be a promising solution for future transportation. The most common example is Tesla.
Main components of an Electric Vehicle (EV):
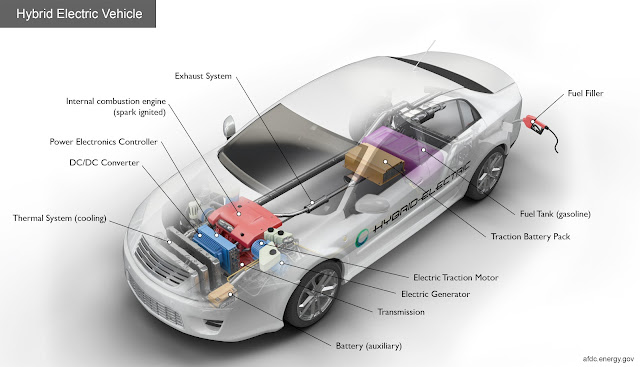
The main components of an electric vehicle system are as below:

- Electric Battery: Battery stores the electricity required to run the vehicle. The battery supplies an electric current to the motor. And thus, the vehicle runs. The higher the capacity of the battery the higher is the range of the electric vehicle. Most modern electric vehicles use Lithium-ion type batteries. These batteries have a higher energy density. It means they are capable of storing more energy.
- Inverter: battery stores the electric current in the form of Direct Current (DC). But, the majority of the motors used in electric vehicles run on Alternating Current (AC). So, the inverter performs the function of converting DC to AC.
- Electric Motor: An electric motor provides the power to rotate the wheels. Motors may be of DC/AC type. However, AC motors are more common.
- Regenerative Braking System: The electric vehicle has only limited energy available. Hence, you need to save every bit of it. This system recovers the energy lost in braking the vehicle and utilizes it to charge the batteries.
- Power Control Unit: The control unit performs the main task. It controls the activities of all the components of an electric vehicle. It monitors the output of the motor, charging of batteries. Also, it provides the necessary information to the driver.
Electric Vehicle (EV) – Meaning
- An electric vehicle (EV) is one that operates on an electric motor, instead of an internal-combustion engine that generates power by burning a mix of fuel and gases.
- Electric Vehicles (EV’s) include road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft.
- Though the concept of electric vehicles has been around for a long time, it has drawn a considerable amount of interest in the past decade amid a rising carbon footprint and other environmental impacts of fuel-based vehicles.
- An electric vehicle may be powered through a collector system by electricity from off-vehicle sources, or maybe self-contained with a battery, solar panels, fuel cells or an electric generator to convert fuel to electricity.
Electric Vehicles can be broadly classified into 8 different types.
- Plug-in Electric Vehicle
- On- and Off-road Electric Vehicles
- Space Rover Vehicles
- Seaborne Electric Vehicles
- Airborne Electric Vehicles
- Electrically Powered Spacecraft
- Range-extended electric vehicle
- Railborne Electric Vehicles
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric vehicles, (PHEVs)
- Battery electric vehicles (BEVs)
- A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery can be recharged by plugging it into an external source of electric power, as well as by its onboard engine and generator.
- Most PHEVs are passenger cars, but there are also PHEV versions of commercial vehicles and vans, military vehicles, utility trucks, trains, motorcycles, buses, and mopeds.
Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV)
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from any external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the Rechargeable battery pack drives.
Plug-in Electric Vehicles can be further categorized into
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
- A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) thus have no internal combustion engine, fuel cell, or fuel tank.
- Some of the broad categories of vehicles that come under this category are trucks, cars, buses, motorcycles, bicycles, forklifts etc.
- Have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- Reduce dependence on petroleum
- Reduce health effects from air pollution
- Reduce dependence on petroleum
- They produce little or no tailpipe emissions
- Internal Combustion engines will consume fuel even when the vehicle is stationary, whereas, in electrical vehicles, the energy is not consumed when it is stationary.
- Electrical Vehicles ‘tank-to-wheels’ efficiency is about a factor of 3 higher than internal combustion engine vehicles
- They can be finely controlled and provide high torque from rest, unlike internal combustion engines, and do not need multiple gears to match power curves. Hence it removes the requirement for gearboxes and torque converters.
- Lesser vibration
- Lesser noise
- Electric motors are mechanically very simple and often achieve 90% energy conversion efficiency over the full range of speeds and power output and can be precisely controlled.
Battery Electric Vehicles
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles – Environmental Advantages
Electric cars (or electric vehicles, EVs) have several environmental benefits compared to conventional internal combustion engine cars.
Electrical Vehicles – Better Energy Efficiency
Electric Vehicles – Mechanical Advantages
- In February 2019, the Union Cabinet cleared a Rs 10,000-crore program under the FAME-II plan. This plan came into power on April 1, 2019. The primary target of the plan is to energize quicker reception of electric and mixture vehicles by offering forthright motivating forces on the acquisition of electric vehicles and furthermore by building up an essential charging framework for EVs.
- In 2017, Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari said something showing India's goal to move to 100% electric vehicles by 2030. Be that as it may, the vehicle business raised worries over the execution of such an arrangement. The public authority in this manner weakened the arrangement from 100% to 30 percent.
- In 2013, India disclosed the "National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020" to make a significant shift to electric vehicles and to resolve the issues of public energy security, vehicular contamination, and development of homegrown assembling capacities. The plan was to offer endowments and make a supporting foundation for e-vehicles.
- The battery manufacturing industry in India can expand than the aggregate sum spent on the import of unrefined petroleum. This would give an immense lift to the Indian economy.
- There should be a cautious intent to hand-hold little and miniature auto part businesses, which utilize huge quantities of individuals. Large numbers of these organizations will not get by as Electric Vehicles supplant petroleum/diesel vehicles. Consequently, it is basic to assist them during the change with staging to EV parts production.
- European Climate Foundation has assessed that through diminishing oil interest by more effective electric vehicles, the business will increment by 5,00,000 to 8,50,000 by 2030.
- According to one of the investigations, net private and social advantages are assessed somewhere in the range of $300 and $400 per Electric vehicle.
- The income misfortune for states from the charges on the oil area is relied upon to be supplanted by higher duty incomes in other monetary areas.
- EVs will set out open doors in tough and lightweight thermoplastics, more popularity for power, stockpiling, and numerous others.
- As per this policy, the focus will be shifted to e-mobility, including e-autos, e-buses, etc. The Government will also offer low-interest rate loans to buy electric vehicles
- A state EV fund will be introduced to cover up the expenditure of the EV Policy
- The main objective of the Electric Vehicle Policy is to reduce air pollution and curb the health emergency issues in the state of Delhi
- These e-vehicles will also reduce the expense of buying motor vehicles.
Electric Vehicles in India – Government Schemes and Initiatives for Promotion of Electric Vehicles
Impact of Electric Vehicles on Employment and Economic Growth
Electric Vehicle Policy (EV) 2020
The Delhi Government has announced the Electric Vehicle Policy 2020 where the emphasis will be given on the replacement of two-wheelers, public transport and shared vehicles and goods-carriers instead of private four-wheelers, with Electric Vehicles (EVs).
Given below are the features of the Electric Vehicle (EV) Policy 2020:

Comments