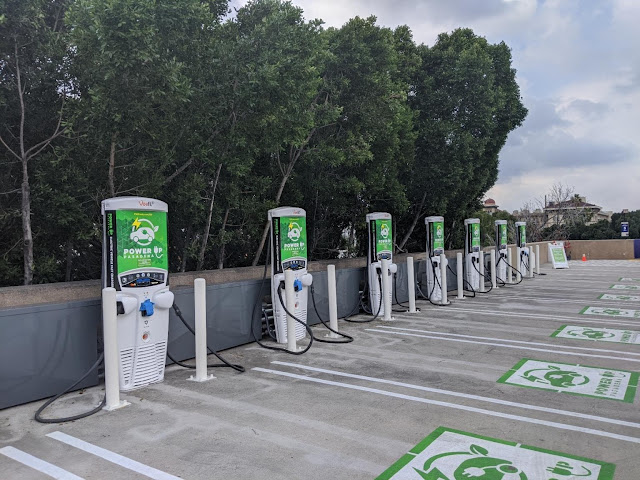
An EV charging station is a piece of equipment that connects your EV to a power supply. Charging stations are fundamental for EVs, as they are what provide the “fuel” for the vehicle; just like gas stations do for conventional vehicles.
How to use an EV Charging Station?
In general, the majority (80%) of charging will take place at home, so it’s likely you will use a home charging point. For an at-home charging station, you simply need to plug in your car.
A public charging station would require more checks before using. You would need to:
- Determine the charging level – You should aim to use either a level 2 or 3 charging station. Level 2 charging stations are, in general, readily available. Level 3 may be used, but are more expensive; better for when you need a quick top-up.
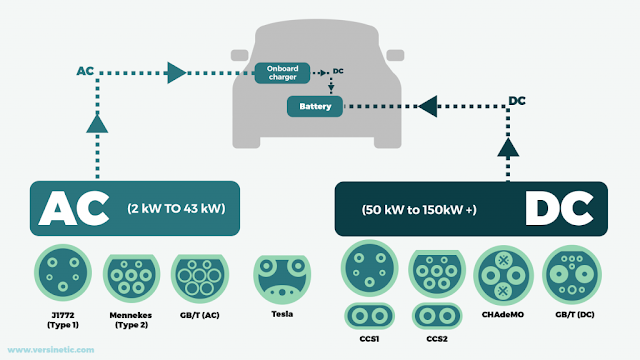
- Check the plug type – This should not be an issue, as these are typically consistent across EVs; unless you have a Tesla and you would need to use Tesla’s superchargers.
- Check the provider – Charging stations are operated by private companies, local governments, or public-private partnerships. You may need a physical card for some or just use your mobile phone. Many providers collaborate, and stations can be easily found via online maps, such as at PlugShare and ChargeMap. Some users did find issues with public charging stations, such as poor charging station design, charging cables not reaching ports, and poor station maintenance.
Is EV Charging Stations Safe?
Safety is of paramount importance for the use of charging stations, so users must be aware of the potential safety hazards.
Fire
Without the proper electrics, the charger could overheat and cause a fire. Some EV chargers may have a temperature sensor to detect overheating.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter Failure
Standard EV charging stations are connected to their power source via a GFCI, in order to prevent electrical shock occurrences. However, reports have revealed a 57 percent failure rate for GFCIs, around the globe. Reasons for this are understood to be associated with lightning, age, wear, and ineffective inspection policies.
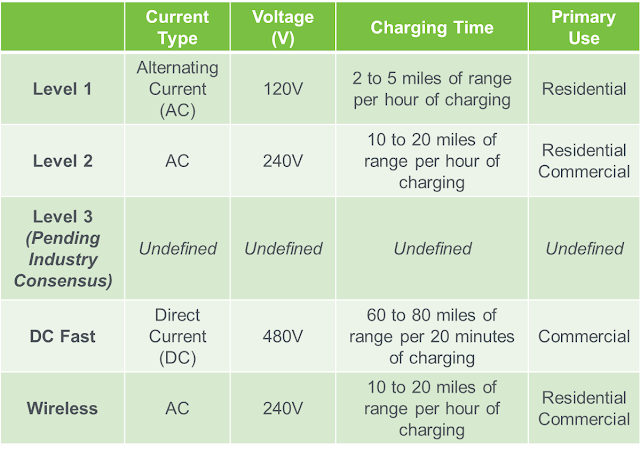
Types of Electric Vehicle Charging
- Level-1 EV Charging (120 Volts): Level-1 electric vehicle charging upholds 120 volts and should be possible utilizing a power line and a control box that accompanies most electric vehicles. Level-1 charging is exceptionally helpful and should be possible at home. Level-1 EV chargers don't bring about any establishment cost and can essentially be connected. The main disadvantage with level 1 chargers is that it requires around 16-18 hours to charge a 60-kWh vehicle.
- Level-2 EV Charging: Level-2 electric vehicle energizing hardware upholds flows to 240V AC and requires introducing electric vehicle supply gear (EVSE) and electric wiring equipped for taking care of higher voltage power. The time taken to charge a battery relies upon its ability and the speed at which it is charged. Charging through Level-2 chargers is a lot quicker than Level-1; a 7 kW EV charger requires 7 to 8 hours to charge a 60-kWh vehicle. Level-2 chargers can be utilized for homegrown or work environment conditions like homes and lofts, little work environments, accommodation, and retail locations.
- Level-3 EV Charging (480 Volts): Level-3 EV charging, likewise called DC quick charging, can energize viable vehicles to 80% in just 30 minutes. Level 3 chargers convert high voltage AC power into DC power for direct capacity in EV batteries. DC quick charging is principally intended for public charging stations. These frameworks are very costly when contrasted with level-1 and level-2 EV chargers. It takes around 20 to 30 mins to re-energize an electric vehicle utilizing DC (level-3) charging. DC (level-3) EV chargers have business applications as they are an ideal choice for vehicle armadas and public vehicles, for example, electric transports, that require quick charging and can oblige an enormous number of vehicles all the while.
Understanding the Components of EV Charging Station
- Battery: At EV charging stations, the batteries are primarily lithium-ion batteries, consisting of cells, packs, battery management system (BMS) to manage control of the charge and discharge of the battery.
- Power Conversion System: The power conversion system for the EV charging station comprises an inverter, its enclosure, and thermal management (HVAC) for batteries to maintain the battery at a specific temperature.
- Software: Electric Vehicle Charging Software is an integral part of EV charging infrastructure. It helps charge point operators and e-mobility service providers to manage EV charging stations and their customers. EV charging software (web or mobile-based) helps in managing the EV chargers at charging stations. Some of the key features of the EV charging software are: connect and monitor the charger, automatic fault detection, live meter display, billing and payments, track costs, manage users, interactive dashboard, and more.
- Vehicle inlet – The socket on the EV which receives the charging power.
- Connector – The end of the charging cable which plugs into the EV.
- Cable – A flexible bundle of conductors which connect the EV to the charging station.
- Plug – The end of the cable which plugs into the charging station. This can vary per region – in the U.S., the plug and socket-outlet are permanently connected.
- Socket outlet – The socket on the charging station in which the cable is plugged
 |
| EV Charging Station TESLA |

Comments